Class 12 Chapter 3 Human Reproduction Question Answer
Human Reproduction
TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS
Q.1. Fill in the blanks:
a) Human reproduce sexually. (asexually/sexually)
b) Humans are viviparous. (oviparous/viviparous/ovoviviparous)
c) Fertilisation is internal in humans. (external/internal)
d) Male and female gametes are haploid. (diploid/haploid)
e) Zygote is diploid. (diploid/haploid)
f) The process of release of the ovum from a mature follicle is called ovulation.
g) Ovulation is induced by a hormone called the Luteineising hormone.
h) The fusion of the male and the female gametes is called fertilisation.
i) Fertilization takes place in the fallopian tube.
j) The zygote divides to form blastocyst, which is implanted in uterus.
k) The structure which provides vascular connection between the fetus and uterus is called placenta.
Q.2. Draw a labelled diagram of male reproductive system.
Ans:
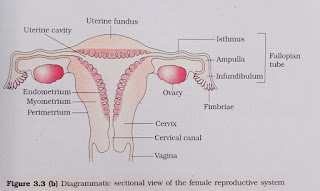
Q.3. Draw a labelled diagram of female reproductive system.
Ans:
Q.4. Write two major functions each of testis and ovary.
Ans: Function of the Testis –
• Testis produces male gametes known as spermatozoa by the process of spermatogenesis.
• The Leydig cells of the seminiferous tubules secret testosterone which is a male sex hormone which helps in the development of secondary sex characteristics in males.
Function of the ovary:
• Ovary produces female gametes known as ova by the process of oogenesis.
• The Graffian follicles secrete estrogen which is a female sex hormone that helps in the development of secondary sex characteristics in females.
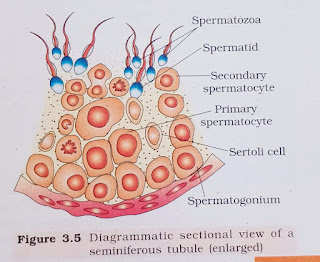
Q.5. Describe the structure of seminiferous tubule.
Ans:
Seminiferous tubules are the structure in where production of sperms takes place in the testes. It is highly coiled structure. These tubules are present in the testicular lobules. Each seminiferous tubule is lined by germinal epithelium. It is lined on its inner side by two types of cells called spermatogonia and sertoli cells. Spermatogonia are male germ cells which generate primary spermatocytes by meiotic divisions. Primary spermatocytes undergo further meiotic division to form secondary spermatocytes and then spermatids finally. Later spermatids metamorphose into male gametes known as spermatozoa. Sertoli cells provide nourishment to the germ cells, so it is also said as nurse cells of the testes. There are large polygonal cells called interstitial cells or Leydig cells just adjacent to seminiferous tubules.
Q.6. What is spermatogenesis? Briefly describe the process of spermatogenesis.
Ans: The process of sperms production from the immature germ cells in males is called spermatogenesis. This process takes place in seminiferous tubules. During the process of spermatogenesis, a diploid spermatogonium i.e., male germ cell increases its size to form a diploid primary spermatocyte. This diploid primary spermatocyte undergoes meiotic division i.e., meiosis I and form two equal haploid secondary spermatocytes. Then each secondary spermatocyte undergoes meiotic division i.e., meiosis II and form two equal haploid spermatids. Hence, a diploid spermatogonium generates four haploid spermatids. These spermatids form spermatozoa by the process called spermiogenesis.
Q.7. Name the hormones involved in regulation of spermatogenesis.
Ans: Follicle-stimulating hormones (FSH) and luteinizing hormones (LH) are the hormones involved in regulation of spermatogenesis.
Q.8. Define spermiogenesis and spermiation.
Answer: Spermiogenesis is the process of transforming spermatids into matured spermatozoa.
Spermiation is the process when mature spermatozoa are produced from the sertoli cells into the lumen of seminiferous tubules.
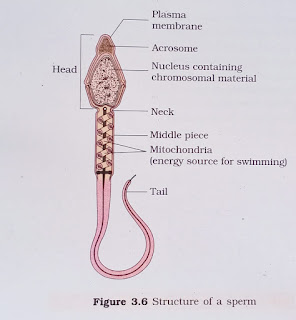
Q.9. Draw a labelled diagram of sperm.
Ans:
Q.10. What are the major components of seminal plasma?
Ans: The major components present in seminal plasma of male reproductive system are mucus, spermatozoa and secretions produced by accessory glands. The seminal plasma is abundant in fructose, calcium, ascorbic acid and certain enzymes. It provides protection and nutrition to the sperms.
Q11. What are the major functions of male accessory ducts and glands?
Ans: The accessory ducts such as vas deferens, vas efferentia, epididymis and rete testis plays an important role in the transport and storage of sperms. The accessory glands such as prostate glands and seminal vesicles secrete fluids which make the reproductive system and sperm soften. This helps the sperm to transport into the female body easier. The fluid is abundant in fructose, calcium, ascorbic acid and certain enzymes. It provides protection and nutrition to the sperms.
Q12. What is oogenesis? Give a brief account of oogenesis.
Ans: Oogenesis is the method of production of a mature ovum from the oogonia in females. It occurs in the ovaries. During the process of oogenesis, a diploid oogonium increases in size and turn into a diploid primary oocyte. The first meiotic division occurs in the diploid primary oocyte which divides the cell into two unequal haploid cells. The smaller cell is called the first polar body and the larger cell is called the secondary oocyte. The secondary oocyte undergoes second meiotic division. A haploid ovum is produced from a diploid oogonium while two or three polar bodies are formed.
Q13. Draw a labelled diagram of a section through ovary.
Ans:
Q14. Draw a labelled diagram of a Graafian follicle.
Ans:
Q15. Name the functions of the following.
a) Corpus luteum
Corpus luteum is produced from the ruptured Graafian follicle. It excretes progesterone hormone during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle. A high level of progesterone prevents the excretion of FSH and LH, thus preventing ovulation. It helps the uterus endometrium to proliferate and make itself ready for implantation.
b) Endometrium
Endometrium forms the inner lining of the uterus. It is abundant in glands which undergoes cyclic alteration during different phases of menstrual cycle.
c) Acrosome
Acrosome is the cap-like structure located in the anterior portion of the sperm head. It presents hyaluronidase enzyme, which hydrolyses the external membrane of the egg, thus helping the sperm to penetrate the egg at the time of fertilization.
d) Sperm tail
Sperm tail is the longest part of the sperm which helps in the movement of the sperm to the female reproductive tract.
e) Fimbriae
Fimbriae are finger-like projection which is present at the end of the fallopian tube. After ovulation, this helps to collect the ovum, facilitated by beating of the cilia.
Q16. Identify True/False statements. Correct each false statement to make it true.
a) Androgens are produced by Sertoli cells.
Ans: False
Androgens are produced by Leydig cells.
b) Spermatozoa get nutrition from Sertoli cells.
Ans: True
c) Leydig cells are found in ovary.
Ans: False
Leydig cells are found in seminiferous tubules present in the testis.
d) Leydig cells synthesise androgens.
Ans: True
e) Oogenesis takes place in corpus luteum.
Ans: False
Oogenesis takes place in the ovary.
f) Menstrual cycle ceases during pregnancy.
Ans: True
g) Presence or absence of hymen is not a reliable indicator of virginity or sexual experience.
Ans: True
Q17: What is menstrual cycle? Which hormone regulates menstrual cycle?
Ans: A series of events which bring cyclic changes inside the female reproductive tract in primates. It takes 28 days to complete one cycle. The end of the cycle is followed by breaking down of endothelium lining which released in the form of blood and mucous from the vagina, which is said to be menses.
The hormones which regulates the menstrual cycle are follicle stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone, estrogen, and progesterone.
Q18. What is parturition? Which hormones are involved in induction of parturition?
Ans: The delivery of the foetus after the complete development of the foetus in the mother’s womb is known as parturition.
The hormones involved in the induction of parturition are oxytocin and relaxin.
Q19. In our society the women are often blamed for giving birth to daughters. Can you explain why this is not correct?
Ans: Human beings possess 23 pairs of chromosome in which 22 pairs are autosomes and one or two kinds of sex chromosomes. Male have either X or Y while the female have only X sex chromosome. The sex of the foetus is determined by the kind of male gamete i.e. X or Y that fuses with the X chromosome of the female. If the X sperm fertilizes with the X chromosome of female, then it will be a girl and if Y sperm fertilizes the X egg then it will be a boy. Hence, it is incorrect to blame women for giving birth to daughters.
Q20. How many eggs are released by a human ovary in a month? How many eggs do you think would have been released if the mother gave birth to identical twins? Would your answer change if the twins born were fraternal?
Ans: One egg is released by a human ovary in a month. Identical twins are produced from a single egg by the division of early blastomere which result from the first zygotic cleavage. Both the babies will have same genes and therefore, called identical twins.
Fraternal twins are born from two eggs. When two eggs are released at the same times which get fertilized by two distinct sperms. Both the babies will have separate genes and therefore, called non-identical twins.
Q21. How many eggs do you think were released by the ovary of a female dog which gave birth to 6 puppies?
Ans: Six eggs were released by the ovary of a female dog which gave birth to 6 puppies.
Post Id: DABP000990