Structure in C | Chapter 9 | Class 10 Computer Science 571(NCERT) Question and Answer | Class 10 Computer Science 571(NCERT) Question and Answer Solutions English Medium |
Structure in C
Chapter 9
1. Define structure in the context of a programming language. How is it different from an array?
(প্ৰগ্ৰেমিং ভাষাৰ প্ৰসংগত গঠন সংজ্ঞায়িত কৰা। এৰেৰ পৰা ই কেনেকৈ পৃথক?)
Ans: Structures (also called structures) are a way of grouping multiple related variables into one space. Each variable in the structure is known as a member of the structure. Unlike an array, a structure can have different data types Int, Float, Mister, etc.
There are three different kinds of arrays: indexed arrays, multidimensional arrays, and associative arrays.
( গাঁথনিবোৰ (যাক গাঁথনি বুলিও কোৱা হয়) হৈছে একাধিক সম্পৰ্কিত চলকক এটা স্থানত গোট কৰাৰ এক উপায়। গাঁথনিটোৰ প্ৰতিটো চলকক গাঁথনিটোৰ সদস্য হিচাপে জনা যায়। এৰেএটাৰ বিপৰীতে, গাঁথনি এটাত বিভিন্ন ডাটা প্ৰকাৰৰ ইণ্ট, ফ্লোট, মিষ্টাৰ আদি থাকিব পাৰে।
ইয়াত তিনিটা পৃথক প্ৰকাৰৰ এৰে আছে: সূচীবদ্ধ এৰে, বহুমাত্ৰিক এৰে, আৰু সহযোগী এৰে।)
2. Is structure a built-in data type? Can we apply basic arithmetic operations such as addition, subtraction to structure variables? Show with a simple C program.
(গঠন এটা বিল্ট-ইন ডাটা টাইপ নেকি? আমি গঠন চলকসমূহত যোগ, বিয়োগ আদি মৌলিক গাণিতিক কাৰ্য্যসমূহ প্ৰয়োগ কৰিব পাৰোনে? এটা সাধাৰণ C প্ৰগ্ৰেমৰ সৈতে দেখুৱাওক।)
Ans: Structure is a built-in - not a data type. We can group different types of constructed information into a structure. Yes, we can apply deductions to basic mathematical tasks such as mixing, structure variables, etc.
(গাঁথনি এটা বিল্ট-ইন - ডাটা প্ৰকাৰ নহয়। আমি বিভিন্ন প্ৰকাৰৰ নিৰ্মিত তথ্যএটা গাঁথনিত গোট কৰিব পাৰোঁ। হয়, আমি প্ৰাথমিক গাণিতিক কাৰ্যযেনে মিশ্ৰণ, গাঁথনি চলকআদিত কৰ্তন প্ৰয়োগ কৰিব পাৰোঁ।)
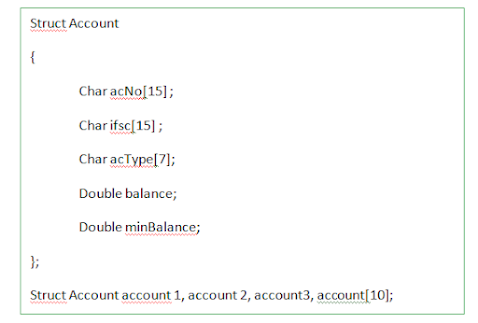
3. Identify the members of the structure from the below code segment.
(তলৰ ক'ড খণ্ডৰ পৰা গঠনৰ সদস্যসমূহ চিনাক্ত কৰক।)
4. Identify the structure variables from the below code segment.
(তলৰ ক'ড খণ্ডৰ পৰা গঠন চলকসমূহ চিনাক্ত কৰক।)
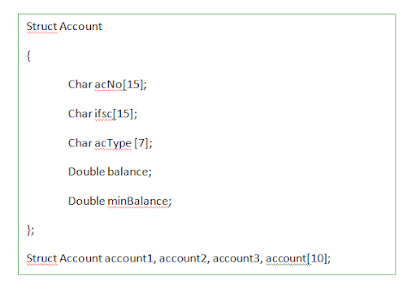
5. Consider the structure below and write statements for the following.
(তলৰ গঠনটো বিবেচনা কৰক আৰু তলৰবোৰৰ বাবে বিবৃতি লিখক।)
a. to declare a variable of the structure
(গঠনৰ এটা চলক ঘোষণা কৰিবলৈ)
Ans: The "structure declaration" provides a type of name and determines different types of variable values (called "members" or "fields"). An alternative identifier called "tag" mentions the type of structure and can be used in the next context of the type 0 of the structure
( "গাঁথনি ঘোষণা"-এ এক প্ৰকাৰৰ নাম প্ৰদান কৰে আৰু বিভিন্ন প্ৰকাৰৰ পৰিৱৰ্তনশীল মান (যাক "সদস্য" বা "ক্ষেত্ৰ" বুলি কোৱা হয়) নিৰ্ধাৰণ কৰে। "টেগ" বুলি কোৱা এক বৈকল্পিক চিনাক্তকৰ্তাই গাঁথনিৰ প্ৰকাৰ উল্লেখ কৰে আৰু গাঁথনিৰ প্ৰকাৰ-ৰ পৰৱৰ্তী প্ৰসংগত ব্যৱহাৰ কৰিব পাৰি)
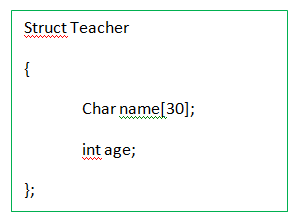
b. to display the age of the teacher
(শিক্ষকৰ বয়স প্ৰদৰ্শন কৰিবলৈ)
Ans:
6. Declare a pointer for structure Teacher (from Q No. 5) and dynamically allocate memory for 10 records.
(গঠন শিক্ষকৰ বাবে এটা পইণ্টাৰ ঘোষণা কৰক (প্ৰশ্ন নং 5 ৰ পৰা) আৰু 10 টা ৰেকৰ্ডৰ বাবে গতিশীলভাৱে মেমৰি আবণ্টন কৰক।)
Ans:
7. Consider the structure below and write statements for the following.
(তলৰ গঠনটো বিবেচনা কৰক আৰু তলৰবোৰৰ বাবে বিবৃতি লিখক।)
a. to declare a pointer for the above structure and display the salary.
(ওপৰৰ গঠনৰ বাবে এটা পইণ্টাৰ ঘোষণা কৰিবলৈ আৰু দৰমহা প্ৰদৰ্শন কৰিবলৈ।)
Ans: To declare a structure pointer struct keyword is used followed by the structure name and pointer name with an asterisk * symbol. Members of a structure can be accessed from pointers using two ways that are. Using dot and asterisk operator on a pointer. Using arrow operator (->) on a pointer
b. to declare a single pointer for two different variables of the higher structure and display the details of the employee whose salary is more.
উচ্চ গঠনৰ দুটা ভিন্ন চলকৰ বাবে এটা পইণ্টাৰ ঘোষণা কৰিবলৈ আৰু যিজন কৰ্মচাৰীৰ দৰমহা বেছি তেওঁৰ বিৱৰণ প্ৰদৰ্শন কৰিবলৈ।
8. Rewrite the program of Q. No. 7 to facilitate dynamic memory allocation for N number of record where N in a user input.
N সংখ্যাৰ ৰেকৰ্ডৰ বাবে গতিশীল মেমৰি আবণ্টন সহজ কৰি তুলিবলৈ Q. নং 7 ৰ প্ৰগ্ৰেমটো পুনৰ লিখক য'ত N এটা ব্যৱহাৰকাৰী ইনপুটত আছে।